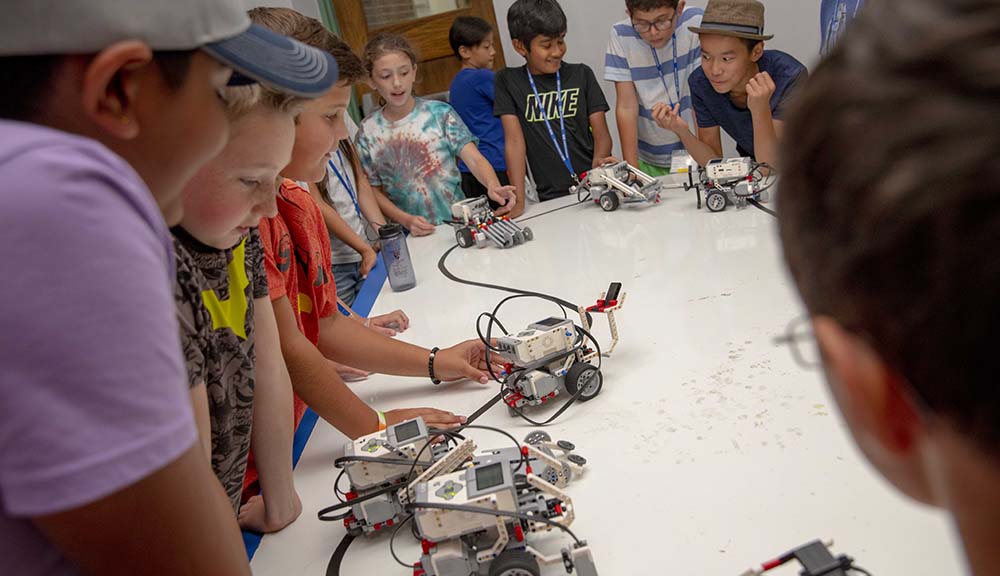
Last month key education stakeholders from 15 African countries met at Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) to explore global best practices and develop strategies to improve math and science opportunities for their students, calling STEM education the “critical lynchpin in a country’s ability to contribute and compete in the global economy.”
Representatives from Niger, Nigeria, Mauritius, Mauritania, Rwanda, Zanzibar, Lesotho, Mozambique, Malawi, Guinea, Benin, Burkina Faso, Togo, Senegal, and Ghana participated in the two-week conference, the first Mathematics and Science for Sub-Saharan Africa Conference (MS4SSA), collaboratively co-organized by The World Bank, WPI, and the New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning (CTL). The event, which included a two-day conference followed by an eight-day workshop, brought over 150 development partners, including the Japan International Cooperation Agency, and STEM education experts from India, China, Africa, and the United States together with the African educational leaders.
The conference highlighted the cross-cultural importance of project-based learning and social constructivism in the development of active learning methods that enable all students to learn and apply science and mathematics. The subsequent eight-day train-the-trainer workshop included hands-on training modules on the use of CTL’s Progressive Science Initiative® (PSI) and Progressive Mathematics Initiative® (PMI) modules on physics, chemistry, biology, and mathematics, as well as WPI modules in materials science and engineering, robotics, and project-based learning.
Wole Soboyejo, dean of engineering and professor of mechanical engineering at WPI, said that one of the goals of the conference was to demystify science and technology for African students, and to encourage these students to feel like “they can do it.”
“The conference offered the opportunity to present a new approach that could be transformative in the lives of young Africans,” says Soboyejo. Referencing the “youth bulge” in Africa, in which 70 percent of African residents are under 30 years old, Soboyejo says a better education boosts individual student learning immediately, and has greater impact on the global level, where more skilled workers create a competitive workforce. “There are a lot of young folks who have to be engaged,” he says. “Electronic access to good information is critical. Then it’s about how you creatively use that information.”
Soboyejo also said that WPI’s project-based curriculum, along with the CTL’s PSI and PMI modules, creates a new teaching and learning paradigm for African schools. “A problem-solving approach used in materials science helps students,” he says. “A diversion from the way things have always been done leads to great things.”
Bob Goodman, executive director of the CTL, reflected on the delegates’ shared vision: "We are tremendously inspired by the opportunity to collaborate with an esteemed group of educational leaders from throughout Sub-Saharan Africa, along with the World Bank and Worcester Polytechnic Institute, to share our preliminary successes in customizing PSI and PMI to address the unique needs of The Gambia’s students and teachers.
“As the pace of modernization accelerates throughout the world, effective STEM education becomes increasingly important in supporting a country’s ability to compete globally. The future lies in innovation. Together we can empower students to collaboratively solve problems and develop their critical thinking, giving them an effective capability to use STEM to problem-solve and innovate in their own lives as well as for their communities, their region, and the world at large."
The participating African delegates expressed their excitement about the modules, and indicated their strong desire to return to their countries to train other trainers on the use of the CTL and WPI modules, which have the potential to stimulate the next generation of Africans to pursue STEM fields and build a highly skilled workforce.
Several delegates noted that demonstrations, including one highlighting inexpensive ways to introduce robotics curriculum into the classroom, were particularly inspiring, as the hands-on excitement of robotics is highly engaging for young students.
The final two days of the workshop included African delegates’ reflections on potential strategies for the rollout of implementation plans the countries had developed during the workshop.
World Bank vice president for the Africa Region Makhtar Diop welcomed the initiative. “Science and technology are a priority for the Africa strategy of the World Bank. This initiative will help countries in Africa leapfrog as they improve students’ learning in and understanding of mathematics and science.”
Lynne Sherburne-Benz, senior regional advisor, Africa Region World Bank, highlighted the importance of the regional dimension of the initiative. “The MS4SSA collaboration aims specifically to utilize and build African expertise institutions," she said, "so that it can help other African institutions improve their capacity to improve teaching of mathematics and science in schools across the continent. The World Bank has successfully supported a number of regional initiatives, and we want this one to grow and expand rapidly.”
About CTL
The New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning (CTL) is an independent, non-profit organization whose mission is to empower teachers to lead change so that all children have access to a high-quality education.
CTL believes the best way to improve education is to invest in teachers by creating changes that make their work less isolated, simpler, more effective, and less stressful. This belief has propelled CTL to an unparalleled track record in rapidly increasing the supply of STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) teachers and advancing student STEM attainment. The New Jersey Education Association created the organization in 2007; and its support and participation continues today. Learn more at https://njctl.org
About The World Bank
With 189 member countries, staff from more 170 countries, and offices in over 130 locations, the World Bank Group is a unique global partnership: five institutions working for sustainable solutions that reduce poverty and build shared prosperity in developing countries. The World Bank is also one of the largest external education financiers for developing countries, managing a portfolio of $14 billion, with operations in 76 countries as of June 2015.